Common Questions About Water Desalination
What is desalination?
Desalination is a process that removes minerals from saline water.
How does the desalination process work?
The two most common desalination methods are thermal and membrane technologies. The thermal process involves heating saline water and then condensing and collecting the water vapor to produce fresh water. Membrane processes, commonly referred to as reverse osmosis (RO), rely on semi-permeable membranes to separate minerals from water.
Are there any desalination plants currently in operation in Texas?
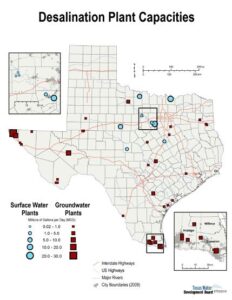
Texas has more than 100 desalination plants. Most are small or intermittent type facilities, but Texas has two large facilities: the Kay Bailey Hutchinson plant in El Paso, which can produce up to 27.5 million gallons of fresh water daily, and the Southmost Regional Water Authority Desalination Plant, which produces 7.5 million gallons a day for south Texas.
A new brackish water desal plant is under construction in San Antonio. Phase 1 of the San Antonio Water System (SAWS) desalination plant is set to be completed in late 2016 and will produce 10 million gallons of fresh water daily. By the time Phase 3 is completed in 2026, the system will produce 25 million gallons of fresh water each day.
All desalination facilities in Texas currently use brackish ground water. There are no marine (seawater) plants in operation in Texas as of March 2016, although several are planned.
How much does water desalination cost?
While there are many variables related to the cost of desalinated water, Texas Water Development Board states a good rule of thumb is $1.10-2.40 per 1,000 gallons for brackish water and $2.46-4.30 per 1,000 gallons for seawater desalination.
Are there desalination plants in other countries?
 About one percent of the world’s population currently receives their drinking water from desalination. There are approximately 12,500 desalination facilities in 120 different countries capable of producing 4 billion gallons per day. Sixty percent of these facilities are located in the Middle East where desalinated water accounts for about 70 percent of the region’s water supply.
About one percent of the world’s population currently receives their drinking water from desalination. There are approximately 12,500 desalination facilities in 120 different countries capable of producing 4 billion gallons per day. Sixty percent of these facilities are located in the Middle East where desalinated water accounts for about 70 percent of the region’s water supply.
Spain recently announced plans to build 21 seawater desalination plants along the Mediterranean coast. Once completed, these plants will have a combined capacity of 527,000 acre-feet per year.
What happens to the salt and minerals that are removed from saline water during the desalination process?
The concentrated saline water that is the unused byproduct of the desalination process is referred to as concentrate. In the case of marine desalination, this byproduct is reintroduced back into the ocean it came from, at a prescribed safe distance from the coastline. When desalination is used inland with brackish water, the concentrate is injected into deep formations via injection wells or, using newer technologies, the minerals can be separated from the concentrate and commercialized. Additional technologies are being developed to better utilize this byproduct.
If you have a question about desalination in Texas, please use the contact us form on this website.